Fentanyl
Fentanyl, the most widely used synthetic opioid in the medical field, has been spreading to the streets mixed with other illegal drugs like heroin and cocaine.
Fentanyl is roughly 40-50 times more potent than heroin and is highly addictive. All it takes is a dose of fentanyl the size of three grains of sand to kill. Consequently, the number of fentanyl-related deaths across North America is rising sharply, especially in FL, OH, MI and PA. At Ambrosia Treatment Center in West Palm Beach, FL, we believe it’s important to know the signs and symptoms of fentanyl abuse and addiction in order to help prevent more deaths.
Street Names
Apache, China Girl, China White, Dance Fever, Goodfella, Jackpot, Murder 8, TNT, Tango & Cash
Common Forms
Powder, Blotter Paper, Mixed With Heroin/Cocaine & Tablets
Common Ways Taken
Injected With Needles, Sucked like Candy & Placed On Skin With A Patch
Signs And Symptoms of Fentanyl Addiction
Short-Term Effects of Fentanyl Abuse
Signs and symptoms of using fentanyl, either medically or illicitly, including:
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Dry mouth
- Retention of urine
- Suppression of breathing
- Severe constipation
- Itching or hives
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Headache
- Difficulty seeing
- Hallucinations
- Shaking
- Overdose
Long-Term Complications from Fentanyl Use
Addiction happens over time. Full physical dependence to a drug requires repeated use, which results in deteriorating health, including:
- Collapsed veins
- Abscesses (swollen tissue with pus)
- Infection of the lining & valves of the heart
- Respiratory depression
- Constipation & stomach cramps
- Liver or kidney disease
- Pneumonia
- Death
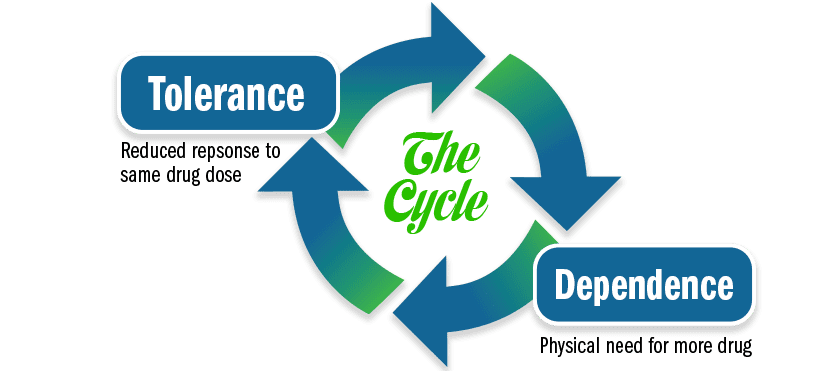
Fentanyl Tolerance & Control
Like heroin, morphine and other opioid drugs, fentanyl works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain that control pain and emotions. Dopamine levels are increased in the reward areas of the brain, creating feelings of euphoria and relaxation.
However, fentanyl quickly creates a tolerance, requiring more of the drug to create that euphoric feeling. Once in the user’s system, the negative effects are extremely difficult to stop, leading to:
- Cravings – Fentanyl addicted individuals are afflicted with both psychological and physiological dependence. Finding it hard to concentrate on anything but the drug, they may not be able to eat, sleep or perform daily activities unless high.
- Compulsion to use – Over time, users develop a physical need that compels them to give into their compulsions and use fentanyl, despite all the havoc the drug wreaks on their lives. Stopping becomes impossible, despite a strong desire to get clean and sober.
- Loss of control – Addicts use more and more each day. Their tolerance builds to the point where they are no longer even chasing the euphoria, but instead using just to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Read the Stories Of Recovery
Ambrosia gave me the tools to be able to live the life I have today. Great staff and an all around great facility. Thank you Ambrosia!
Gary R
Ambrosia helped me too. I let go of anger, resentment and started trusting my husband again. I actually still text Wellness regularly. I learned the hard way that not all treatment centers are the same, and I know from experience that Ambrosia is the right choice.
Michelle F
The therapy at Ambrosia changed my opinion of therapy overall. Without their help, I would’ve never talked about the things that I worked through while I was here. It’s a supportive environment with the structure needed to heal and grow as a person. This experience helped me get in touch with who I am outside of being an addict.
Antonio R
Ambrosia changed my daughter’s life. That’s not an exaggeration. She had been to several other facilities, with little, short-lived success, but Ambrosia was the only one that kept her sober for over a year now. She’s a whole new person!
Missy S
What Every Parent Needs to Know
Overdose is common.
Opioid receptors exist in the areas of the brain that that control breathing. High doses of any opioid can cause breathing to stop completely, which leads to death. The high potency of fentanyl substantially increases the risk of overdose. The drug is often sold mixed with heroin or cocaine, which can increase the danger of overdose as well, especially since the user is unaware if or how much fentanyl is included.
Addiction is likely.
Because fentanyl is so addictive, users will not be able to quit on their own and will often use more of the drug each time. As fentanyl is used more often and in more amounts, the likelihood of devastating consequences increase. Even if overdose is avoided, chronic users can suffer from consequences like liver disease or pneumonia.
Naloxone is an opioid receptor antagonist that reverses opioid overdose and restores normal respiration. Overdoses of fentanyl should be treated immediately with naloxone and may require higher doses to successfully reverse the overdose.
The access to this medication varies by state. Because of the sad fact that emergency personnel often come too late, the recent legislative trend is to increase the access to everyone. In the states below, Naloxone is available without a prescription at pharmacies like CVS.
Arkansas • California • Florida • Massachusetts • Minnesota • Mississippi • Montana • New Jersey • North Dakota • Pennsylvania • Rhode Island • South Carolina • Tennessee • Utah • Wisconsin
Because of the dangerous complications (including death), stopping fentanyl should only be attempted in the care of medical professionals. With a safe drug detox, addicts are kept comfortable and cared for, so they want to continue the process of recovery. The supervision also prevents relapse, which would be much more likely to cause overdose since the drugs are no longer built-up in their system.
The symptoms usually start 12 hours after the last drug use and can last up to three days, including:
- Flu-like symptoms
- Intense cravings
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Cramping in the limbs
- Cold sweats
- Runny nose
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Fever
- Death
Addiction is a disease, not a choice. Several factors can make an individual more susceptible to a fenanyl addiction, including:
Genetics
Individuals with a first-degree relative with addiction disorder are more prone to become addicted themselves, though genetics alone are not the only factor.
Use of Other Drugs
Repeated drug use changes the way the brain reacts and responds to stimuli. Opiates disrupt communication inside and between the brain’s cells. More drug is needed to compensate for lack of neurotransmitters, which leads to seeking a stronger drug like fentanyl.
Environmental
Socioeconomic factors, as well as family beliefs and peer influence, affect an individual’s choices about drugs. Environmental factors may also include difficult circumstances or life events (trauma), where drugs are used as a way to cope.
Psychological
Untreated or undiagnosed mental illness (including depression or anxiety) plays a role in drug use. This may lead to self-medicating with illegal drugs to tolerate or cope with symptoms of the disorder or illness.