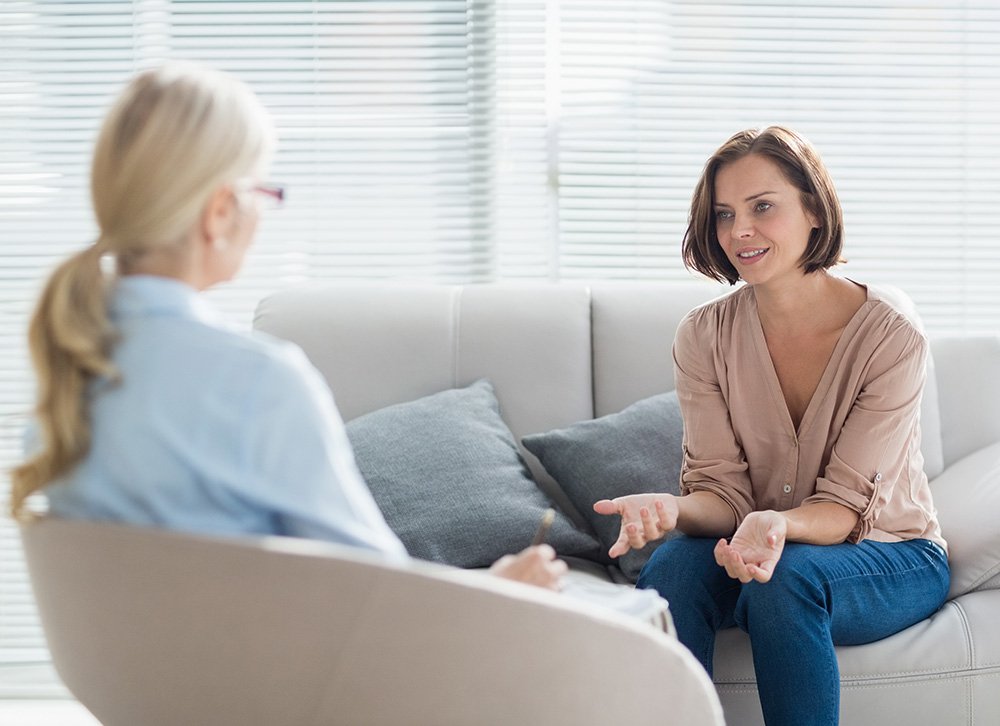
What Are The Signs Of Drug Addiction?
When a person is addicted to drugs, they might go to great lengths to hide their addiction. Identifying a drug addiction can be difficult for concerned friends, family, and loved ones. Your loved ones might not seem like themselves, and you start to wonder what could be going wrong. Knowing the signs of drug addiction can help you identify the causes of your loved one’s change and help you when seeking treatment.
Global Epidemic
Addiction is a complex disease that can affect anyone, regardless of race, creed, ethnicity, and upbringing. The initial decision to take drugs is usually voluntary, but after repeated and regular use, tolerance forms which is one of the first tell-tale signs of a developing dependency. Over time, the brain changes which inhibits an addicted person’s self-control and ability to resist urges to take drugs.
Addiction does not only affect the addict, but it also has a rippling effect on the addict’s family and friends, especially if they are a close, supportive unit.
Understanding the Signs of Addiction
Understanding the signs of addiction can give you a better sense of the situation. Some signs of drug addiction can be from other things, like an underlying mental health disorder or a medical issue. You don’t want to jump to conclusions; however, you also don’t want to ignore any signs of drug abuse.
Though your loved one might try to hide their addiction, some signs start to appear more and more as the addiction worsens. Drug addiction is treatable, and anyone can quit; however, it is best to get ahead of these issues early on.
Physical Signs of Addiction
Physical signs of addiction are things that you will see or manifest as symptoms similar to other illnesses. Remember that addiction is a disease, and you will see some physical symptoms like any other disease.
Physical signs of addiction include:
- Runny nose
- Bloodshot eyes
- Tremors, shakiness, or seizures
- Strange odors on the person, in their room, car, or other areas
- Weight change
- Sleeping too little or too much
- Staying up late, sleeping in, or irregular sleep patterns
- Change of appetite
- Trouble with coordination
- Unable to sit still or hyperactivity
- Extreme tiredness
- Jaw clenching
- Needle marks
- Sloppy appearance or a lack of personal hygiene
- Physical evidence, like vape pens, pipes, needles, and other drug paraphernalia
Some of these signs could indicate other issues. You also want to be sure to look for new behaviors or changes that cannot be explained in another way. For example, if your loved one experienced a loss in the family, weight change and irregular sleeping could be a sign of grieving or depression triggered by loss.
Behavioral Signs of Addiction
Behavioral signs of addiction include:
- Change in primary friendships and reluctance to introduce you to new friends
- Being secretive, especially about what they are doing and who they spend time with
- Withdrawing from the family
- Mood swings, irritability, or agitation
- Isolating and spending more time alone than normal
- Loss of interest in hobbies and enjoyable activities
- Decline in performance at work or school
- Disciplinary issues at work or school, like tardiness, absences, and disputes
- Legal issues
- Dangerous behaviors, like unsafe sex or reckless driving
- Not fulfilling responsibilities at work, home, or with the family
- Asking for money or having financial issues
When you notice these behaviors, along with physical signs of addiction, your loved one might be abusing drugs. Drug addiction can affect people from all walks of life. Your loved one did not begin using drugs planning to become addicted. They might have been self-medicating for an underlying issue, like chronic pain, stress, or mental illness.
Not everyone who uses drugs will become addicted. Your loved one might be at a higher risk based on several different factors.
Why Do Some People Become Addicted While Others Do Not?
There is no single factor that can predict whether or not someone will become addicted to substances, but there are various factors that influence the likelihood of substance abuse, such as:
- Biological Factors
- Environmental Factors
- Early Developmental Factors
What Are the Risk Factors of Drug Addiction?
Risk factors of drug addiction include:
- Family history of substance use disorders or alcoholism
- Underlying mental health issues, like:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Bipolar disorder
- Child history of physical or sexual abuse
- Traumatic events
- Problems growing up or a dysfunctional family
- Troubling fitting in with others or forming meaningful friendships
- Peer pressure or being around others who use drugs
- Using drugs at a young age
Often, many of these risk factors of addiction are present at one time, or one leads to another. For example, growing up in a dysfunctional home could lead to underlying depression, difficulty forming healthy friendships, and drug use to cope with these issues.
Risk factors for addiction also need to be addressed during substance use treatment. When you don’t address the underlying causes of addiction, you might find replacement addictions, like gambling, or you could be at a greater risk of relapse. Substance abuse treatment centers can help you overcome your addiction and the underlying issues at the root of the addiction.
Leading researchers in the field of addiction estimate between 40-60% of a person’s likelihood of becoming addicted to either drugs and/or alcohol lies between genetic and environmental factors. The effects of environmental factors enhance the functions of a person’s genes, increasing the individual’s chance of becoming addicted to any substance.
Adolescents and people with mental disorders are at much greater risk of drug abuse because their brain is in developmental stages. As their brain undergoes dramatic changes, the part of the brain that enables us to make formative decisions, moderate social behavior, and allows expression of the personality, also known as the prefrontal cortex, is maturing over an extended period.
During this process, the adolescent’s decisions influence the growth rate and ultimately long-lasting consequences of the brain’s development. Addiction is a developmental disease that often starts out as voluntary, but can soon lead to a full-blown, overpowering, seemingly helpless condition.
Drug addiction is a preventable disease that begins with education. Knowledge about family history of drug addiction or alcoholism is an essential component in education in the early years of development. Programs in school settings that include family, educators, communities, and the media to discuss youth trends, the harmful repercussions of drug abuse, and outreach to those who are affected.
Drug Addiction Treatment in South Florida
Drug addiction can happen to anyone. You or your loved one might be at greater risk of abusing drugs due to certain biological, environmental, and developmental factors. Ambrosia Treatment Center of South Florida is here to help you identify the signs of addiction so that you can get help for you or your loved one. Call us today or visit our admissions page to learn more.